The sight of a tree falling, albeit a natural phenomenon, can be highly unnerving. The unpredictability and severity of many tree failures often raise concerns about safety and property damage. While it isn’t possible to see the future, understanding why trees fall and taking preventive measures can help safeguard ourselves and our loved ones. In this blog, we unpack common reasons why trees topple over and explore steps you can take to mitigate potential risks.
Understanding Why Trees Fall
Trees may seem sturdy and steadfast, but beneath the surface lies a complex network of roots and soil that anchors trees in place. Unearthing the reasons behind tree falls requires a closer look at root and soil health.
The Role of the Root System
The root system of a tree plays a vital role in its stability and overall health. Roots absorb water and essential nutrients from the soil, transporting them upward to nourish the canopy. They also store energy through starches and produce growth hormones necessary for development. But most important to our discussion here, roots provide physical support by anchoring the tree into the ground. Any compromise to root structure and root health undermines the tree’s stability, making it more susceptible to toppling. Here are some common culprits of poor root health and stability.
- Root Rot
Root rot is a fungal infection that targets the roots, gradually weakening them and hindering their ability to provide stability. As the infection spreads, the roots lose their structural integrity, jeopardizing the entire tree. Regular arborist inspections can help identify early signs of root rot, enabling timely intervention through treatments or, in more severe cases, tree removal to prevent potential falls.

- Shallow Root Systems
Trees with shallow root systems are particularly vulnerable to external stresses, such as wind, heavy rain, or human activities. Shallow roots provide less resistance against forces that may uproot the tree, making the tree more susceptible to being toppled during storms or adverse weather conditions. Proper irrigation, planting appropriate species, and avoiding compacted or restricted spaces can encourage the growth of more profound, robust root systems.
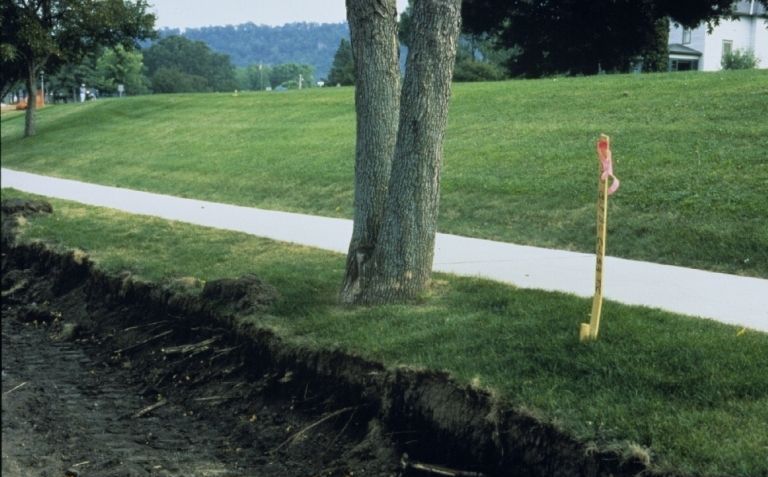
- Root Damage
Physical damage to the roots can result from various factors, including construction, landscaping, or diseases. Projects that change the soil, like trenching and regrading, can inadvertently harm tree roots, leading to a gradual decline in stability. Diseases targeting the roots, such as Armillaria root rot, can cause irreparable damage. Try to exercise caution during construction and landscaping near trees, using techniques like mulching and Tree Protection Zones to minimize root disturbance and protect the tree’s foundation.
Soil Composition
The soil surrounding a tree may not be the first thing that comes to mind when considering stability, but it plays a crucial role. Wet and saturated soils can decrease a tree’s stability significantly. When soil becomes waterlogged, it loses its ability to provide the necessary support for the roots. This is especially true in areas with poor drainage or after heavy rains, where water accumulates around the roots and compromises the foundation. So, be extra cautious around trees in wet soils, especially after sudden, heavy storms.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Risks
Now that we’ve touched on some common reasons for trees falling, here are some proactive measures to mitigate these risks. Go through this checklist so you can reduce the risk of your tree falling and, in the case of emergencies, be well-informed on what to do.
Proper Watering and Mulching Techniques
- Watering
A well-hydrated tree is a resilient tree. Proper watering helps maintain tree health and root stability. Inadequate moisture can lead to shallow root systems and stress, making the tree more susceptible to diseases and root-related issues. Deep watering, where the soil is saturated to reach the entire root zone, encourages roots to grow deep into the soil, anchoring the tree more securely. Learn more on how to water trees!
- Mulching
Mulching is a simple yet effective technique that provides a protective layer around a tree’s base. This layer helps retain soil moisture, regulates soil temperature, and suppresses competing weeds. Proper mulching also protects against mechanical damage caused by lawnmowers or trimmers, minimizing the risk of root injury. However, make sure to apply mulch correctly. Avoid “mulch volcanoes” or piling mulch against the tree trunk, which can cause root rot. Spread the mulch out to the tree’s dripline, space allowing, in a layer 2-4” thick.

The Role of Pruning in Tree Stability
Pruning is essential for maintaining a tree’s structural integrity, extending beyond aesthetics. Structural pruning involves strategically removing branches to optimize weight distribution and reduce the risk of imbalances that could lead to toppling. By eliminating dead or weak branches, especially those prone to breakage, the tree has a reduced load and reduced potential for unexpected falls.
In windy areas, specific wind-resistant pruning techniques, such as reducing branch end weight and removing competing leaders, further fortify trees against uprooting during storms. Consult a certified arborist on appropriate pruning techniques for specific tree species and local conditions.
What to Do When a Tree Falls
Despite our best efforts in preventive measures, unforeseen circumstances, and extreme weather can lead to a tree falling. Knowing how to respond promptly and safely is important in such situations. Here are two key steps to take when faced with a fallen tree.
Immediate Safety Precautions
- Assess the Immediate Surroundings
When a tree falls, first ensure the safety of people and property in the vicinity. Immediately assess the area to identify potential hazards, such as downed power lines, unstable branches, or compromised structures. Keep a safe distance from the fallen tree and any associated dangers.
- Evacuate and Secure the Area
If the fallen tree poses an imminent threat, evacuate and block off the hazardous zone using caution tape, cones, or barriers. In the event of structural damage or electrical issues, contact the relevant authorities, such as emergency services or utility companies, to address any immediate dangers.

Contacting Professional Arborists
When dealing with a fallen tree, seek professional arborists with the knowledge and skills to conduct tree removal with minimal risk to people and property. At A Plus Tree, safety is our top priority! Our highly trained and certified arborists use state-of-the-art equipment and adhere to the highest safety standards throughout removal. We carry comprehensive liability insurance and workers’ compensation, offering peace of mind for property owners. Don’t hesitate to contact us for swift and secure emergency tree removal services in need!