If you’ve noticed unusual rust-colored spots on the leaves of your plants or trees, you might be dealing with a common issue known as rust. This fungal disease can affect a wide variety of plants, leading to unsightly foliage and possibly, severe damage if left untreated. Read on to find out what rust disease is, what causes it, the symptoms to watch for, how to prevent it, and what the treatment options are!
What is Rust Disease?
Rust disease is an umbrella term for a group of fungal infections that affect plants and trees, causing distinct rust-colored spots on leaves and stems. The fungi responsible for rust disease belong to the Pucciniales order, which includes thousands of species. These fungi are obligate parasites, meaning they can only survive on living plant tissue. Rust disease can be more than an aesthetic issue. The fungus also weakens plant health by interfering with photosynthesis and stressing the plant over time.
Rust fungi have a complex life cycle often involving multiple host plants. They produce spores that spread through the air, water, or physical contact, infecting new plants and continuing the cycle of disease. Rust disease is more common in warm and humid climates, where the conditions are ideal for fungal growth and spore dispersal.
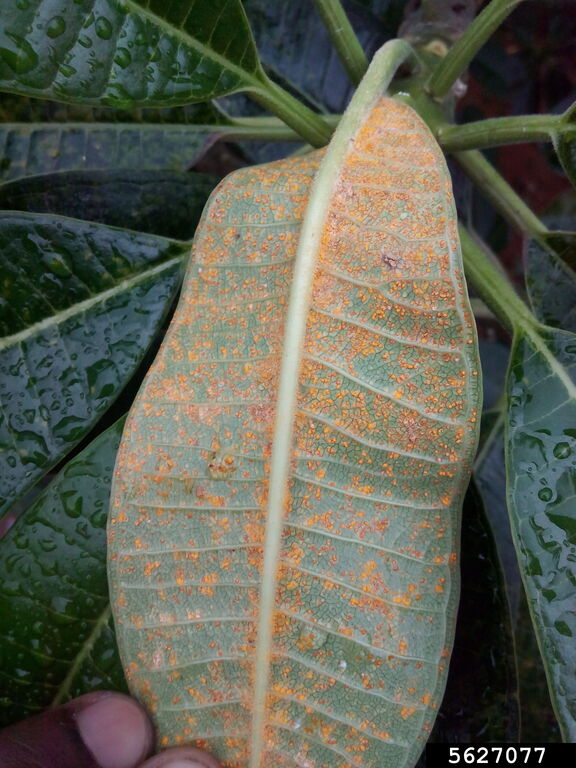

What Causes Rust Spots on Leaves?
Rust spots occur on leaves after they’re infected with rust fungi. These fungi thrive in specific environmental conditions, typically under high humidity and moderate temperatures. The main causes of rust spots are:
- Humidity: Rust fungi require moisture to germinate and infect plant tissues. High humidity levels, especially when combined with poor air circulation, create the perfect environment for rust spores to thrive.
- Temperature: Most rust fungi prefer moderate temperatures, about 55°F to 75°F (13°C to 24°C). These conditions mostly occur during spring and fall, making these seasons peak times for rust disease outbreaks.
- Water: Overhead watering can increase the likelihood of rust infection by wetting the leaves and encouraging spore germination. Water splashing from infected soil or plants can also spread rust spores.
Symptoms of Rust Fungi
Identifying rust fungi early can help you take prompt action to control the disease. Here are the key symptoms to look out for:
- Rust Spots: The most obvious sign is the appearance of small, rust-colored spots on the upper and lower surfaces of leaves. These spots can vary in color from yellow to orange to reddish-brown.
- Pustules: The rust spots may develop into raised pustules that release spores. These pustules are usually found on the underside of leaves and can give the leaf a bumpy texture.
- Leaf Yellowing: Infected leaves may turn yellow around the rust spots, eventually leading to overall yellowing of the leaf.
- Leaf Drop: Severe infections can cause leaves to curl, wilt, and drop prematurely. This defoliation weakens the plant or tree.
- Stem and Flower Infections: In some cases, rust fungi can also infect stems, flowers, and fruit, leading to distorted growth and reduced plant productivity.

How to Prevent Rust Fungus?
Prevention is key to managing rust fungus and keeping your trees healthy. Here are some effective strategies to prevent rust infections:
- Proper Spacing: Provide adequate spacing between trees to improve air circulation. This reduces humidity around the foliage, making it less favorable for rust fungi to thrive.
- Proper Pruning: Follow proper pruning practices to increase air flow through leaves and branches, which will discourage rust infection. But be careful not to remove too much live foliage since this will starve and weaken the plant.
- Watering Practices: Avoid overhead watering. Instead, use drip irrigation or water the base of trees to keep the foliage dry. Water early in the day so that any moisture on leaves can evaporate quickly.
- Sanitation: Remove and destroy any infected leaves, stems, or plant debris. This helps to eliminate sources of rust spores that can reinfect plants.
- Resistant Varieties: Choose rust-resistant tree varieties when possible. Many nurseries have resistant strains that are less susceptible to rust fungi.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of mulch around the base of plants to reduce soil splash and prevent spores from reaching the foliage.
How Do I Treat Rust Fungus on Plant & Tree Leaves?
If rust fungus has already infected your plants, there are several steps you can take to treat the disease and minimize its impact:
- Remove Infected Parts: Prune away and dispose of infected leaves, stems, and other plant parts. This helps to reduce the spread of spores to healthy tissue.
- Apply Fungicide: Apply fungicides labeled for rust control. Look for products containing active ingredients such as sulfur, copper, or myclobutanil. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully for the best results.
- Improve Air Circulation: Trim surrounding vegetation and thin out dense plantings to enhance air movement. This helps to dry out foliage and reduce the humidity that rust fungi need.
- Apply Tree Health Care: Promote tree health with proper fertilization and watering. Healthy plants are more resistant to diseases, including rust fungi.
By understanding rust disease and implementing these preventive measures and treatments, you can protect your trees from this common fungal problem and keep them looking their best. If you need professional assistance with diagnosing and treating rust disease, contact our tree care experts for help!