Don’t ignore boring bugs! No, not the snoozefest, uninteresting kind. But the kind that destroy trees. They bore into the trunk and branches, tunneling into and eating the wood.
They are the most dangerous insect pests because they weaken and can kill entire trees. Not only are the trees sick and ugly, they are liabilities prone to collapse and branch failure. Two common boring bugs to watch out for in the PNW are Bronze Birch Borer and Cherry Bark Tortrix.
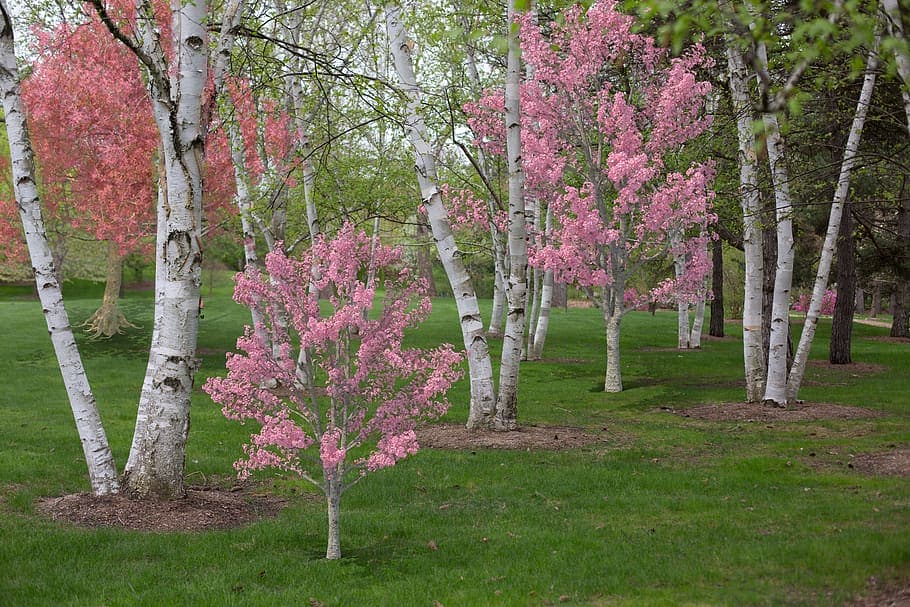

Birch trees and ornamental cherries are highly susceptible to boring pests.
What Are Bronze Birch Borers and Cherry Bark Tortrix?
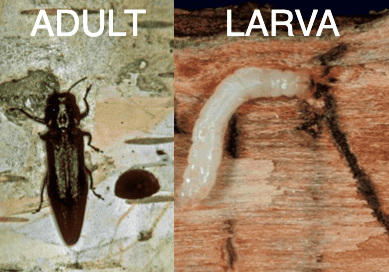
Bronze Birch Borer
All birch trees are at risk of these black beetles, native North America. In spring, adults lay eggs inside bark crevices. The larvae form feeding galleries inside the tree trunk and emerge as adults around May.
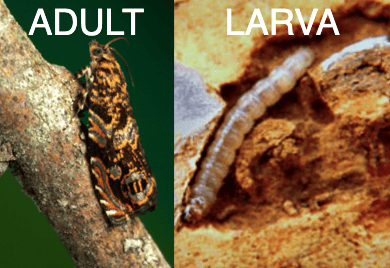
Cherry Bark Tortrix
In the 1980's, these European moths were discovered in the PNW. Adults lay eggs on bark, often near wounded or infected areas. Larvae feed and overwinter in the trunk, emerging in April to repeat the cycle.
Tree Species Affected
Bronze Birch Borer: All Birch Trees.
Cherry Bark Tortrix: Ornamental Cherry, Mountain Ash, Almond, Apple, Crabapple, and other Fruit Trees.
What's the Damage?
Both Bronze Birch Borer and Cherry Bark Tortrix tunnel into wood, causing the following damages:
- Canopy dieback.
- Exit holes on bark.
- Bark swelling and sap ooze.
- Weakened trees and branches.
- Tree death and failure.
- Property damage and liabilities.
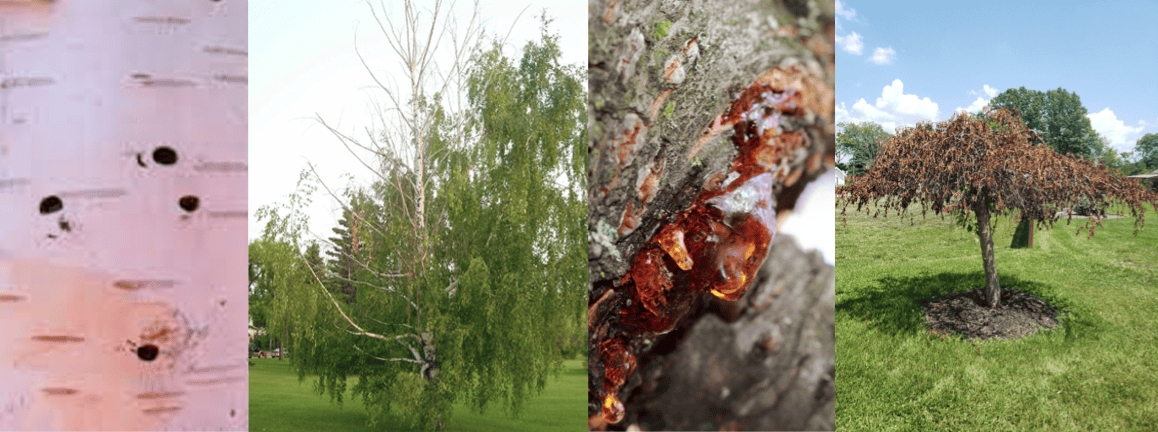

Left to Right: Bark holes & canopy dieback from Bronze Birch Borer, sap ooze and tree death from Cherry Bark Tortrix.
What's the Treatment?
Treat your trees with a trunk injection of Emamectin Benzoate, which provides protection for 2 years. Success all depends on timing! Apply before adults emerge and start laying eggs. Treat for Cherry Bark Tortrix by April and Bronze Birch Borer by May.
Plan ahead so you time it right and win the fight!