Ash trees, scientifically known as the genus Fraxinus, are a prominent feature of many landscapes due to their graceful appearance and lush foliage. Unfortunately, these trees are increasingly threatened by various diseases and pests that can cause significant harm and even tree death. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the most common ash tree diseases and pests, their symptoms, signs, and, most importantly, methods of prevention and treatment. By understanding these diseases and pests, you can safeguard the health and vitality of your cherished ash trees.
Introduction to Ash Tree Diseases
Ash trees are vulnerable to various diseases and pests, each with its symptoms and potential for damage. Here are the main diseases and pests we will delve into:
- Emerald Ash Borer (EAB): A highly destructive invasive insect that attacks and kills ash trees.
- Ash Anthracnose: A fungal disease that affects the leaves, twigs, and branches of ash trees.
- Ash Yellows: A viral disease that causes a decline in tree health and vitality.
- Ash Rust: A fungal disease characterized by visible rust-colored growth on leaves, stems, or branches.
- Root Rot: A condition caused by various fungi affecting the roots of ash trees.
- Banded Ash Borer: A wood-boring beetle that can cause severe damage to ash trees.
- Verticillium Wilt Disease: A soil-borne fungal disease that affects the vascular system of ash trees.
Common Symptoms and Signs
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of ash tree diseases and pests is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. Small holes in the bark, galleries in the wood, and increased woodpecker damage are telltale signs of wood-boring pests like emerald ash borers and banded ash borers. Discolored or yellowing leaves are often indicators of fungal or viral diseases, although trees stressed from pests will also weaken and can develop yellow leaves. The presence of mushrooms at the tree base indicates root rot, which also stunts tree growth and wilts leaves. Branch dieback and defoliation can happen from both disease and pest damage as the tree weakens over time. Recognizing these symptoms early on helps save ash trees because heavily diseased or infested trees are difficult to treat successfully, often ending in removal. So, watch for these common key indicators of diseases and pests!
Now, let’s delve into the damage caused by these diseases and methods of prevention and treatment.
Emerald Ash Borer (EAB)
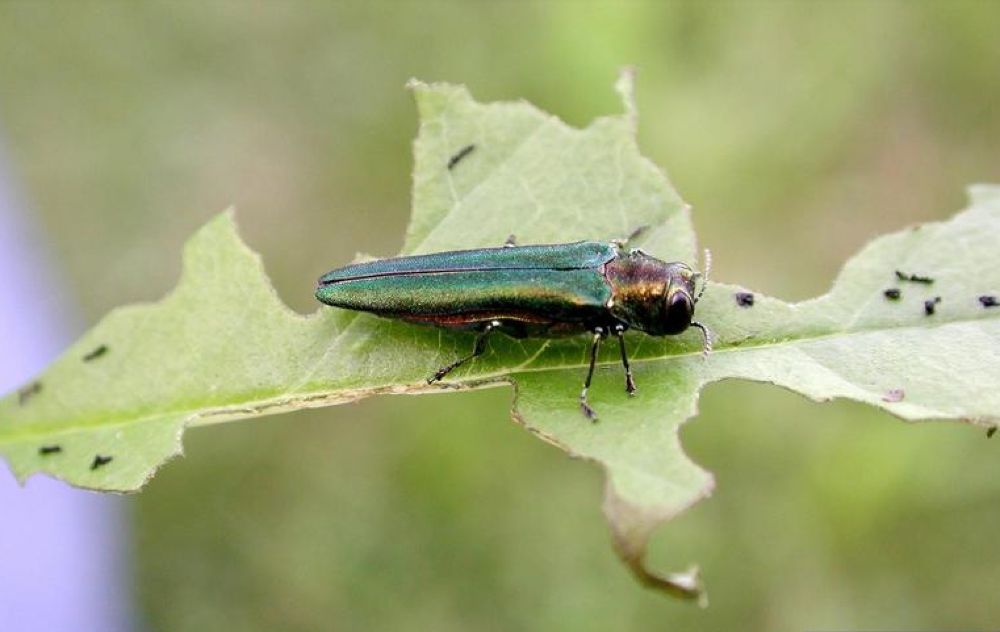

Symptoms and Signs:
– D-shaped exit holes: About 1/8 inch in diameter, left by emerging adult borers.
– S-shaped galleries: Underneath the bark, created by larval feeding.
– Thinning canopy: Foliage at the top of the tree becomes sparse and yellow.
– Vertical bark splits: On the trunk as the infestation progresses.
Damage:
Emerald Ash Borers cause extensive damage by feeding on the inner bark of ash trees, disrupting nutrient and water transport. Without enough nutrients and water, trees start to die back. Dead trees become brittle and weak, increasing the likelihood of failure and damage to surrounding property and people.
Prevention and Treatment:
– Insecticides: Specific insecticides can protect ash trees from EAB infestation. Visit our EAB page to learn more!
– Early Detection and Removal: Promptly remove and destroy infested trees to prevent further spread.
Ash Anthracnose Disease
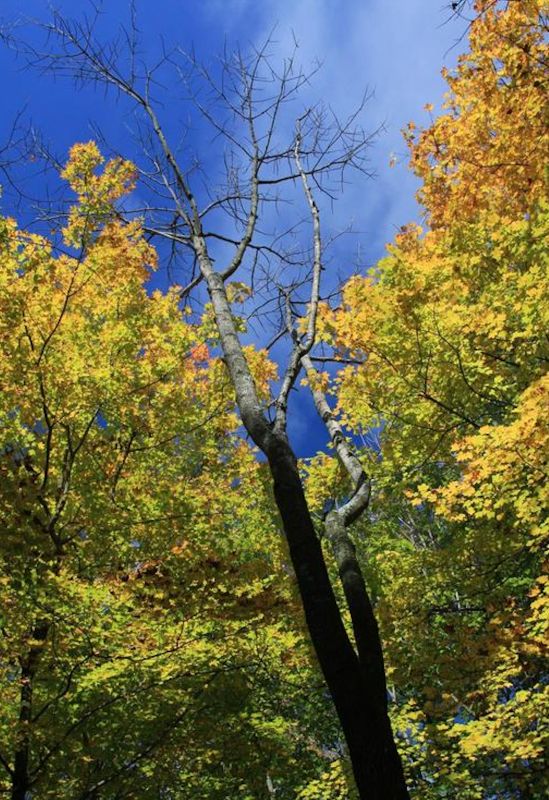

Symptoms and Signs:
– Irregular leaf spots: Dark, water-soaked lesions on leaves, often with a purplish border.
– Premature defoliation: Leaves drop early, weakening the tree and affecting overall health.
– Twig dieback: Dying and blackening of smaller branches.
Damage:
Ash Anthracnose affects the leaves, leading to reduced photosynthesis and weakening of the tree.
Prevention and Treatment:
– Fungicides: Regular applications of fungicides can help manage anthracnose, especially during wet seasons.
– Proper Pruning: Prune affected branches to improve air circulation and reduce disease severity.
– Fertilization and Tree Health Care: Ensure proper nutrients and care to strengthen the tree’s resistance. Just like people, healthy trees are less likely to get sick!
Ash Yellows
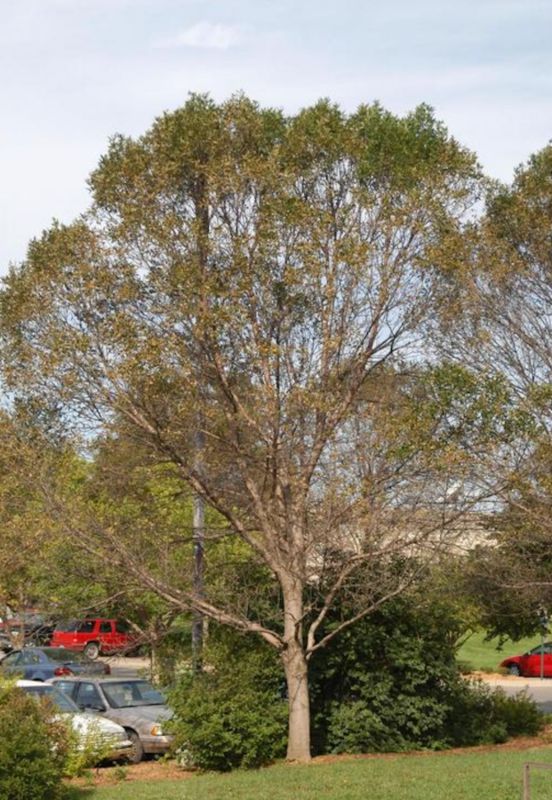

Symptoms and Signs:
– Yellowing and wilting of foliage: Particularly evident in the upper crown.
– Stunted growth: Reduced leaf size and overall growth vigor.
– Thicker, darker bark: May crack or split as the disease progresses.
Damage:
Ash yellow is a viral disease that weakens trees, impacting growth and vitality.
Prevention and Treatment:
– Plant Resistant Varieties: Select ash tree varieties with higher resistance to ash yellows.
– Regular Monitoring: Inspect trees for symptoms and promptly remove infected trees.
– Proper Soil Management: Maintain well-drained soil and avoid compacting the root zone.
Ash Rust

Symptoms and Signs:
– Rust-colored growth: Small, raised structures on leaves, stems, or branches.
– Yellow-orange pustules: Visible on the underside of leaves.
– Leaf curling and distortion: Abnormal growth due to the infection.
Damage:
Ash rust weakens the tree by affecting leaf function and causing defoliation.
Prevention and Treatment:
– Fungicides: Apply fungicides to control rust outbreaks during the growing season.
– Leaf Removal and Pruning: Remove and destroy affected leaves to minimize disease spread.
– Promote Tree Vigor: Maintain tree health through proper watering, fertilization, and pruning.
Root Rot

Symptoms and Signs:
– Reduced growth: Trees may appear stunted or smaller than expected.
– Yellowing and wilting leaves: Despite adequate water, leaves may droop and yellow.
– Mushrooms near the tree’s base: Fruiting bodies of the root rot fungi.
Damage:
Root rot affects the root system, impairing the tree’s ability to take up water and nutrients.
Prevention and Treatment:
– Proper Drainage: Ensure good drainage to prevent waterlogged soil, a breeding ground for root rot.
– Healthy Soil Management: Maintain soil health to reduce stress on the tree and enhance root growth. Mulch trees properly by not “volcano mulching” or piling mulch against the trunk, which traps moisture and attracts fungi.
– Fungicide Treatment: If your tree is planted in an area prone to root rot, preventative applications of fungicide can be beneficial. After root rot has set in, success rates of fungicide applications are very low.
Banded Ash Borer
Symptoms and Signs:
– Serpentine (S-shaped) galleries: Channels from larvae just beneath the bark.
– Banding patterns on bark: Larval feeding marks that resemble bands.
– Woodpecker damage: Pecking holes to access larvae, indicating infestation.
Damage:
Banded Ash Borers damage ash trees by tunneling through the wood, weakening the structure.
Prevention and Treatment:
– Preventive Insecticides: Apply insecticides to protect the tree from borer infestations. Utilize trunk injection or systemic insecticides to target borers effectively.
– Pruning and Tree Inspection: Regularly inspect the tree for signs of infestation and prune affected branches.
Verticillium Wilt Disease

Symptoms and Signs:
– Wilting and yellowing leaves: Typically on one side or branch of the tree.
– Brown streaks in the sapwood: Visible when infected branches are cut open.
– Sudden dieback of branches: Portions of the tree or entire branches may die off rapidly.
Damage:
Verticillium wilt affects the vascular system, inhibiting water and nutrient transport. Without water and nutrients, the tree cannot survive.
Prevention and Treatment:
– Resistant Tree Selection: Plant Verticillium-resistant ash tree varieties.
– Fungicide Applications: Apply appropriate fungicides to manage the disease, especially in the early stages.
– Maintain Tree Health: Optimal care, including proper irrigation and fertilization, can help trees resist infection.
When to Call a Professional
If you observe severe symptoms of widespread infestation or are unsure about the best action for treating ash tree diseases, seek assistance from a certified tree care professional. At A Plus Tree, we have the expertise and tools to accurately diagnose issues, recommend appropriate treatments, and implement measures to preserve the health of your ash trees.
By following these guidelines and promptly addressing any signs of disease and pests, you can protect your ash trees and ensure their longevity in your landscape. If you have any questions or need more information, please ask us or check out our Pest & Disease Management Services!